This comprehensive worksheet explores the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It’s designed to help students understand the structures and functions of these essential building blocks of life. The worksheet covers topics such as cell wall composition, DNA storage, and the presence of organelles. It also includes diagrams for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, allowing students to visually compare and contrast their features.
Introduction
This worksheet delves into the fascinating world of cells, the fundamental units of life. It focuses on two major categories of cells⁚ prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells, like bacteria, are simpler and smaller, lacking a membrane-bound nucleus. Eukaryotic cells, found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists, are more complex and larger, with a nucleus that houses their genetic material. This worksheet will guide you through the key differences between these two cell types, helping you understand their unique structures and functions. You’ll explore their distinct characteristics, including the presence or absence of organelles, the way they store DNA, and their methods of reproduction. Get ready to embark on a journey through the microscopic world and gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity and complexity of life on Earth.
Prokaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells are the simplest and most ancient form of life on Earth. They are single-celled organisms, lacking a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Their DNA is circular and located in a region called the nucleoid, which floats freely within the cytoplasm. Prokaryotes have a cell membrane that encloses the cell, and many also have a rigid cell wall for structural support. Some prokaryotes possess additional layers, such as a capsule, which provides a sticky surface for attaching to surfaces. These tiny cells play crucial roles in various ecosystems, including decomposition, nitrogen fixation, and the production of antibiotics. Examples of prokaryotic organisms include bacteria and archaea, which are found in diverse environments ranging from hot springs to human intestines.
Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells are far more complex than prokaryotic cells, possessing a membrane-bound nucleus that houses their genetic material. This nucleus contains the cell’s DNA in the form of linear chromosomes. Eukaryotic cells also feature a wide array of membrane-bound organelles, each specialized for a specific function. These organelles include mitochondria for energy production, chloroplasts for photosynthesis (in plant cells), the endoplasmic reticulum for protein synthesis and lipid metabolism, the Golgi apparatus for packaging and distributing cellular products, and lysosomes for cellular digestion. Eukaryotic cells are characteristic of multicellular organisms, such as plants, animals, fungi, and protists. They exhibit a greater level of complexity and organization compared to prokaryotic cells, enabling them to carry out more intricate biological processes.
Key Differences
The primary distinction between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells lies in the presence or absence of a membrane-bound nucleus. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells possess a well-defined nucleus that encloses their DNA. Eukaryotic cells also exhibit a greater level of complexity, boasting a variety of membrane-bound organelles that carry out specialized functions. In contrast, prokaryotic cells are simpler, with their DNA located in a region called the nucleoid, which is not enclosed by a membrane. Furthermore, eukaryotic cells tend to be larger than prokaryotic cells. These fundamental differences in structure and organization reflect the diverse roles these cell types play in the living world.
Worksheet Structure
The worksheet is carefully structured to guide students through a comprehensive exploration of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It typically begins with an introduction that defines these cell types and highlights their significance in biology. The worksheet then delves into the specific features of each cell type, covering aspects like cell wall composition, DNA storage, and the presence of organelles. A key section often compares and contrasts prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in a table format, making it easy for students to identify their key differences. The worksheet may also include diagrams of both cell types, providing a visual aid for understanding their structures. Finally, it concludes with questions that assess students’ understanding of the material, encouraging them to apply their knowledge to real-world examples.
Prokaryotic Cell Diagram
The prokaryotic cell diagram is a crucial component of the worksheet, providing students with a visual representation of this simple cell type. The diagram typically depicts a circular shape, representing the cell’s lack of a defined nucleus. Key structures are labeled, including the cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA. The diagram may also highlight the presence of flagella or pili, which are involved in movement and attachment, respectively. The diagram serves as a visual tool for students to understand the arrangement of internal structures and their relative sizes within a prokaryotic cell. It helps them visualize the concept of a simple, single-celled organism and its basic functional components.
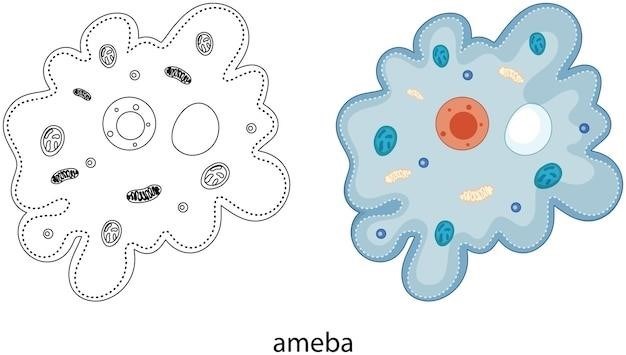
Eukaryotic Cell Diagram
The eukaryotic cell diagram is a more complex representation compared to its prokaryotic counterpart. This diagram typically showcases a larger, more intricate structure with a clearly defined nucleus. It emphasizes the presence of membrane-bound organelles, each with specialized functions. Commonly labeled structures include the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, and vacuoles. The diagram might also depict the cell wall in plant cells, distinguishing them from animal cells. The eukaryotic cell diagram serves as a visual guide for students to grasp the organization and complexity of these cells. It helps them understand the compartmentalization of functions within the cell and how different organelles work together to maintain cellular processes.
Answer Key
The answer key for the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells worksheet is a valuable tool for both students and educators. It provides the correct answers to all the questions presented in the worksheet. This key is crucial for students to check their understanding of the concepts covered and identify areas where they may need further clarification. For educators, the answer key serves as a reference point to assess student learning and adjust teaching strategies as needed. It helps ensure that students are grasping the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including their structures, functions, and evolutionary relationships. The answer key also provides a framework for discussions and further exploration of these essential cellular concepts.
The prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells worksheet, along with its answer key, serves as a valuable tool for understanding the fundamental building blocks of life. By exploring the differences between these two cell types, students gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity and complexity of living organisms. This knowledge is crucial for further exploration of biological concepts, including the mechanisms of cell division, inheritance, and the evolution of life on Earth. The worksheet and answer key provide a solid foundation for understanding the intricate world of cells and their vital role in maintaining life as we know it.
Further Exploration
Beyond the basic differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, there is a vast world of knowledge to uncover. Students can delve deeper into the specific roles of various organelles within eukaryotic cells, exploring their intricate mechanisms and contributions to cellular functions. Investigating the evolutionary relationships between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, including the theory of endosymbiosis, offers fascinating insights into the origins of complex life. Additionally, studying the diverse adaptations of prokaryotic cells, such as their ability to thrive in extreme environments, reveals the remarkable resilience and adaptability of these simple yet vital organisms. The journey of understanding cells is ongoing, and further exploration opens doors to a captivating world of scientific discovery.
Resources
For further learning and exploration, there are numerous resources available online and in libraries. Websites like Khan Academy and Biology Online provide interactive lessons, animations, and quizzes on prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Textbooks such as Campbell Biology and Biology by Raven and Johnson offer in-depth coverage of cellular biology. Scientific journals like Nature and Science publish cutting-edge research on cell structure and function. Educational videos on platforms like YouTube can provide visual explanations of complex concepts. Additionally, museums and science centers often host exhibits on cellular biology, offering hands-on learning experiences. By utilizing these resources, students can deepen their understanding of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and embark on a fascinating journey of scientific discovery.